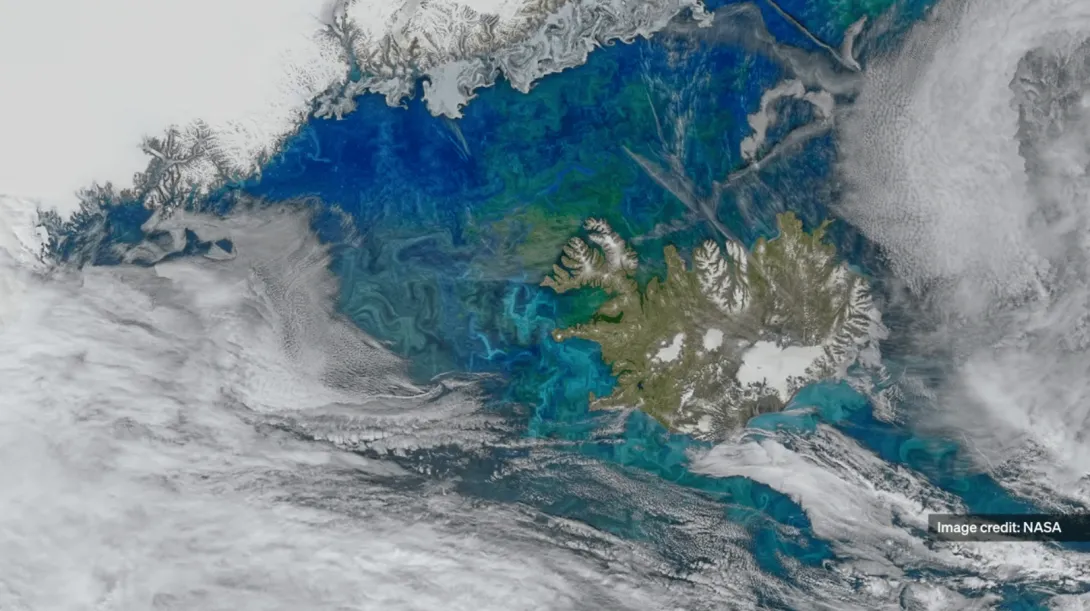
The ocean’s role in climate change
The ocean plays a powerful role in regulating Earth’s climate. It absorbs heat and carbon dioxide, drives weather patterns, and supports life on a planetary scale. But as the climate changes, the ocean is also changing: warming, acidifying, and behaving in new and less predictable ways.
Studying the ocean helps us understand what’s happening to our climate, where tipping points may be reached, and how the impacts will unfold across the globe—from rising sea levels to shifting weather extremes.
How does climate change impact the Ocean?
Climate change is accelerating, and we’re already seeing the effects: hotter summers, stronger storms, flooding coasts, and disrupted ecosystems. But there’s still time to respond. Understanding how the ocean is changing is vital for designing effective adaptation and mitigation strategies. Whether it’s forecasting storms, managing carbon, or protecting coastal communities, ocean science gives us the evidence we need to act.
How is NOC responding?
At the National Oceanography Centre, we lead and support global efforts to understand climate change through the lens of the ocean. Our research combines long-term data, advanced modelling, autonomous monitoring technologies and international partnerships.
We work across disciplines, from physical oceanography and biogeochemistry to socio-economic systems, to provide insight that can inform decisions at every level: from coastal communities to global climate policy.
Engage With Climate Conversations

Massive Open Online Course (MOOC): Ocean Science in Action
We believe in open science and shared learning.That’s why we’ve created resources like our free Massive Open Online Course (MOOC): Ocean Science in Action — helping students, researchers, and decision-makers explore how marine technology is being used to solve environmental challenges.